6. Preprocessing options 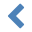



Converting a DITA document to formats such as HTML, PDF, RTF,
etc, comprises two steps. First step consists in preprocessing the DITA
document. Second step consists in translating the preprocessed DITA document
to the other format by the means of XSLT stylesheets.
The XSLT
stylesheets are parameterized by using , while the preprocessor is parameterized by using
. The latter menu item displays a dialog box which is
described in this section.
Figure 10. The Preprocessing Options dialog
box
The top combobox allows to select the group of options to be edited.
Each group of options is completely separated from the other. For example,
specifying that an index is to be generated as backmatter for group
"Convert to single-page XHTML" will have an effect
when you'll use and no effect at all when you'll use or when you'll use (because there is a separate "Convert to
single-page XHTML" group of options for the
Map, BookMap and
Topic configurations).
- Default language
- Specifies the main language of the document. Examples:
en, en-US, fr, fr-CA. This
information is needed in order to sort the index entries. By default,
this information is taken from the
@xml:lang attribute
of the root element of the topic map (if any, "en"
otherwise).
- Table of Contents
- Specifies whether to automatically generate a Table of
Contents and, if a Table of Contents is to be generated,
where to generate it. Frontmatter means at the beginning
of the document. Backmatter means at the end of the
document.
This option, like List of Figures, List of
Tables, List of Examples and Index, is mainly useful
when working with maps or individual topics. When working with a
bookmap, the preferred way to specify the location, if any, of a
Table of Contents is to do it in the bookmap itself. In all
cases, what's specified in the bookmap has priority over the value of
this option.
- List of Figures
- Specifies whether to automatically generate a List of
Figures and, if a List of Figures is to be generated, where
to generate it.
- List of Tables
- Specifies whether to automatically generate a List of
Tables and, if a List of Tables is to be generated, where
to generate it.
- List of Examples
- Specifies whether to automatically generate a List of
Examples and, if a List of Examples is to be generated,
where to generate it.
- Index
- Specifies whether to automatically generate an Index and,
if an Index is to be generated, where to generate it.
- Copy images to
- Copy the image files referenced in the topics to specified
directory. If specified path is relative, it is relative to the output
directory.
In the above screenshot,
"images/*.{png,jpg,jpeg,gif}" means:
- copy to directory images/, relative to the output
directory,
- as is (that is, without having to convert the image to another
image format),
- all the images referenced in the document source, having a
png, jpg, jpeg or gif filename
extension.
- Any image referenced in the document source having a filename
extension other than png, jpg, jpeg or
gif (e.g. svg, tif) will be
automatically converted to an image having a png,
jpg, jpeg or gif filename
extension.
When this field is left empty, the generated document will
reference the image files using absolute URLs. This is harmless for
PDF, RTF, etc, files because at the end of the conversion process,
such files will embed a copy of the image files. However, this
is rarely what is wanted for HTML-based formats (XHTML, Java Help,
HTML Help, Eclipse Help, EPUB, etc).
- Chunk mode
- Allowed values are Automatic,
Single and None.
Chunk Automatic means: ignore the chunk
specification found in the topic map and output a single chunk for the
Print medium; honor the chunk specification for
the Screen medium.
Chunk
None means ignore the chunk specification found
in the topic map and output a single chunk. As explained above, chunk
None is implicit for some formats (PostScript,
PDF, RTF, etc).
Both the None and
Single values may be used to force the
generation of a single output file. Chunk
Single allows to reuse a map designed to output
multiple HTML pages in order to generate a single HTML file or a PDF
file.
- Target medium
- Explicitly specifies the output medium:
Screen (XHTML, HTML Help, Eclipse Help, etc) or
Print (PDF, RTF, etc). By default, the output
media is guessed using the extension of the output file.
- Preprocessor messages
- Specifies the level of verbosity of the preprocessor. Allowed
values are (from not verbose to very verbose):
None, Information,
Verbose, Debug.
Some fields may be ``grayed out'' (disabled). This happens in two
cases:
- The DITA configuration has been customized by the local guru. This
automatically prevents the end user from making any change to the
preprocessing options.
- Changing the values of some options (e.g. Target
medium) would break the stock configuration.